This is the 9th WHAM example. We assume you already have
wham installed and are relatively familiar with the
package. If not, read the Introduction and Tutorial.
In this vignette we show how to calculate retrospective predictions,
by peeling x years of data, re-fitting models, and then
projecting each peel y years. Although this can be done for any
variable, we demonstrate how to do so for recruitment, as in Fig. 4 of
Xu et al. (2018). We use
the same data and model setup as for m3 and m5
from example
2.
1. Load data
# devtools::install_github("timjmiller/wham", dependencies=TRUE)
library(tidyverse)
#> Warning: package 'ggplot2' was built under R version 4.2.3
#> Warning: package 'tibble' was built under R version 4.2.3
#> Warning: package 'tidyr' was built under R version 4.2.3
#> Warning: package 'purrr' was built under R version 4.2.3
#> Warning: package 'dplyr' was built under R version 4.2.3
#> Warning: package 'stringr' was built under R version 4.2.3
library(wham)Create a directory for this analysis:
# choose a location to save output, otherwise will be saved in working directory
write.dir <- "choose/where/to/save/output"
dir.create(write.dir)
setwd(write.dir)We need the same data files as in example
2. Let’s copy ex2_SNEMAYT.dat and CPI.csv
to our analysis directory:
wham.dir <- find.package("wham")
file.copy(from=file.path(wham.dir,"extdata","ex2_SNEMAYT.dat"), to=write.dir, overwrite=TRUE)
file.copy(from=file.path(wham.dir,"extdata","CPI.csv"), to=write.dir, overwrite=TRUE)
asap3 <- read_asap3_dat("ex2_SNEMAYT.dat")
env.dat <- read.csv("CPI.csv", header=T)2. Specify models
Setup models m5 (with CPI effect on recruitment) and
m3 (no CPI effect on recruitment) from example
2:
full state-space model (numbers-at-age are random effects for all ages,
NAA_re = list(sigma='rec+1',cor='iid'))logistic normal age compositions (
age_comp = "logistic-normal-pool0")Beverton-Holt recruitment (
recruit_model = 3)Cold Pool Index (CPI) fit as an AR1 process (
ecov$process_model = "ar1")CPI has a “limiting” (e.g. carrying capacity, Iles and Beverton (1998)) effect on recruitment (
ecov$where = "recruit",ecov$how = 2)
env <- list(
label = "CPI",
mean = as.matrix(env.dat$CPI), # CPI observations
logsigma = as.matrix(log(env.dat$CPI_sigma)), # CPI standard error is given/fixed as data
year = env.dat$Year,
use_obs = matrix(1, ncol=1, nrow=dim(env.dat)[1]), # use all obs (=1)
lag = 1, # CPI in year t affects recruitment in year t+1
process_model = "ar1", # fit CPI as AR1 process
where = "recruit", # CPI affects recruitment
how = NA) # fill in by model in loop
# 2 models, with and without CPI effect on recruitment (both fit CPI data to compare AIC)
# Model Recruit_mod Ecov_mod Ecov_how
# m1 Bev-Holt ar1 ---
# m2 Bev-Holt ar1 Limiting
df.mods <- data.frame(Model = c("m1","m2"), Ecov_how = c(0,2), stringsAsFactors=FALSE)
n.mods <- dim(df.mods)[1]
df.mods3. Fit the models
for(m in 1:n.mods){
env$how = df.mods$Ecov_how[m]
input <- prepare_wham_input(asap3, recruit_model = 3,
model_name = df.mods$Model[m],
ecov = env,
NAA_re = list(sigma="rec+1", cor="iid"),
age_comp = "logistic-normal-pool0") # logistic normal pool 0 obs
input$par$logit_selpars[1:4,7:8] <- 0
# fit model
mod <- fit_wham(input, do.retro=F, do.osa=F)
saveRDS(mod, file=paste0(df.mods$Model[m],".rds"))
plot_wham_output(mod=mod, dir.main=file.path(getwd(),df.mods$Model[m]), out.type='png')
}4. Look at convergence and diagnostics
mod.list <- file.path(write.dir,paste0("m",1:n.mods,".rds"))
mods <- lapply(mod.list, readRDS)
ok_sdrep = sapply(mods, function(x) if(x$na_sdrep==FALSE & !is.na(x$na_sdrep)) 1 else 0)
df.mods$conv <- sapply(mods, function(x) x$opt$convergence == 0) # 0 means opt converged
df.mods$pdHess <- as.logical(ok_sdrep)Compare model output - they are pretty similar.
names(mods) <- c("m1 (no CPI)","m2 (CPI)")
res <- compare_wham_models(mods, fdir=write.dir, do.table=F, plot.opts=list(kobe.prob=FALSE))5. Run retrospective predictions
For each model, peel 3-15 years of data and re-fit the model using
retro(), and then project each peel 3 years by calling
project_wham(). These projections are done with F
= 0 and continuing the CPI AR1 process model (without new observations).
You can specify alternative options for the projections using
$proj.opts (see project_wham()
and Ex
3: Projections).
n.yrs.peel <- 15
n.yrs.proj <- 3
for(m in 1:n.mods){
mods[[m]]$peels <- retro(mods[[m]], ran = unique(names(mods[[m]]$env$par[mods[[m]]$env$random])), n.peels=n.yrs.peel, save.input = T)
for(p in 3:n.yrs.peel) mods[[m]]$peels[[p]] <- project_wham(mods[[m]]$peels[[p]], proj.opts = list(n.yrs = n.yrs.proj, proj.F=rep(0.001,n.yrs.proj)))
}6. Plot retrospective predictions of recruitment
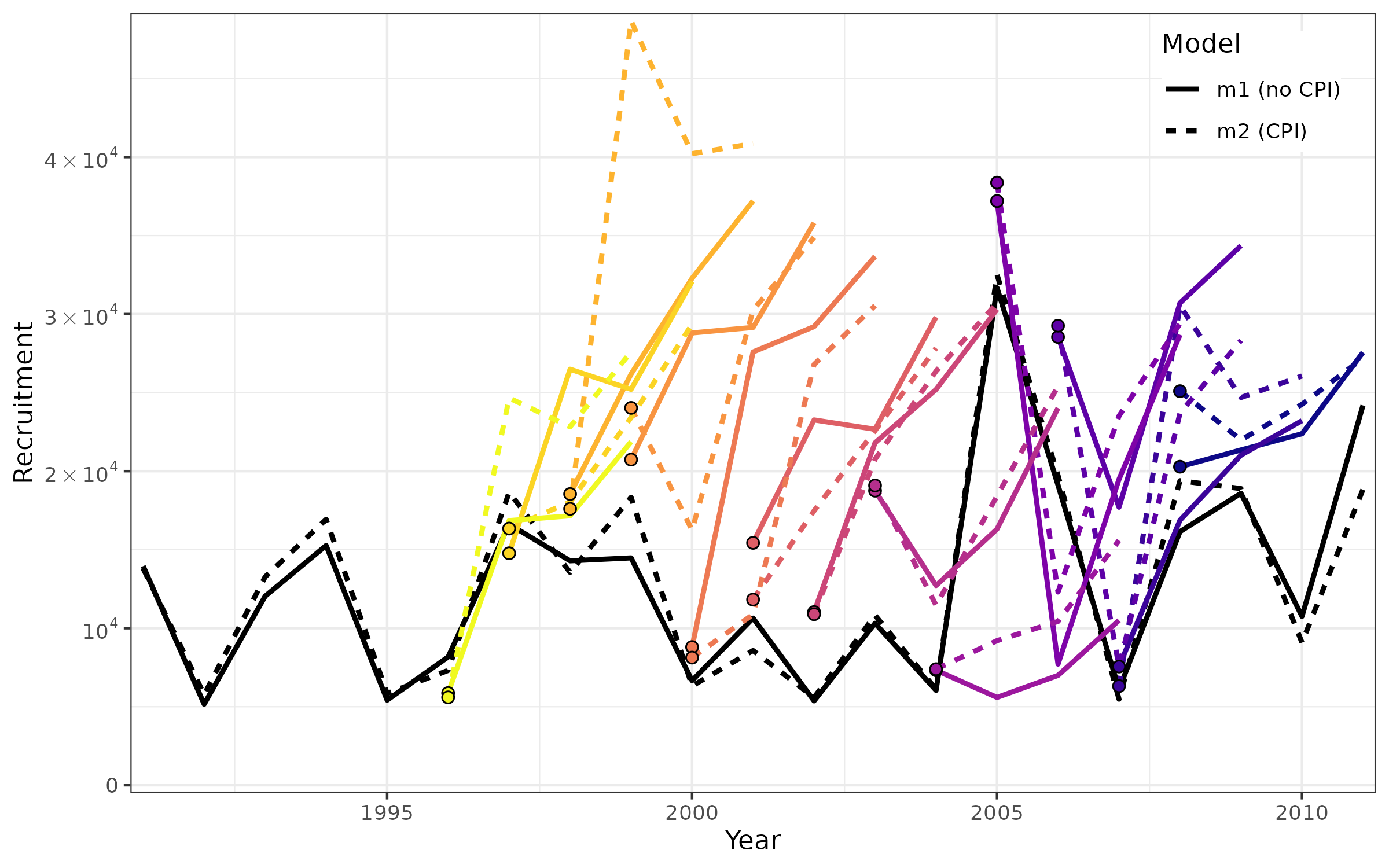
Here is a function to extract and plot the retrospective predictions of recruitment from each model. It can easily be modified to extract other variables of interest, e.g. SSB or F.
plot_retro_pred_R <- function(mods, peels=3:n.yrs.peel, n.yrs.proj=n.yrs.proj){
df <- data.frame(matrix(NA, nrow=0, ncol=6))
colnames(df) <- c("Year","Model","Peel","Recruitment","termyr")
for(m in 1:length(mods)){
for(p in peels){
tmp <- read_wham_fit(mods[[m]]$peels[[p]])
df <- rbind(df, data.frame(Year=tail(tmp$years_full, n.yrs.proj+1),
Model=names(mods)[m],
Peel=p,
Recruitment=tail(exp(tmp$log_NAA[,1]), n.yrs.proj+1),
termyr=c(1,rep(0,n.yrs.proj))))
}
# get full model fit, "peel 0"
tmp <- read_wham_fit(mods[[m]])
df <- rbind(df, data.frame(Year=tmp$years,
Model=names(mods)[m],
Peel=0,
Recruitment=exp(tmp$log_NAA[1:length(tmp$years),1]),
termyr=0))
}
df <- filter(df, Year > 1990)
df$Model <- factor(df$Model, levels=names(mods), labels=names(mods))
df$Year <- as.integer(df$Year)
df$Peel <- factor(df$Peel)
dfpts <- filter(df, termyr==1)
cols <- c("black", viridis::viridis_pal(option="plasma")(length(levels(df$Peel))-1))
g <- ggplot(df, ggplot2::aes(x=Year, y=Recruitment, linetype=Model, color=Peel, fill=Peel, group=interaction(Model,Peel))) +
geom_line(size=1) +
geom_point(data=dfpts, color='black', size=2, pch=21) +
scale_x_continuous(expand=c(0.01,0.01)) + # breaks=scales::breaks_extended(5)
scale_colour_manual(values=cols) +
scale_fill_manual(values=cols) +
guides(color = FALSE, fill=FALSE) +
scale_y_continuous(expand=c(0.01,0.01), limits = c(0,NA), labels=fancy_scientific) +
theme_bw() +
theme(legend.position=c(.9,.9), legend.box.margin = ggplot2::margin(0,0,0,0), legend.margin = ggplot2::margin(0,0,0,0))
return(g)
}
plot_retro_pred_R(mods, peels=3:n.yrs.peel, n.yrs.proj=n.yrs.proj)
ggsave(file.path(write.dir,"retro_pred_R.png"), device='png', width=8, height=5, units='in')The two black lines represent the “true” recruitment from each model, i.e., the recruitment estimates when fitting to the full data. Points and lines are colored by peel from yellow (1996) to dark blue (2008). The points are terminal year recruitment estimates and lines are projected recruitment (3 years).