Ex 3: Projecting / forecasting random effects
Source:vignettes/ex3_projections.Rmd
ex3_projections.RmdIn this vignette we walk through an example using the
wham (WHAM = Woods Hole Assessment Model) package to run a
state-space age-structured stock assessment model. WHAM is a
generalization of code written for Miller et al. (2016)
and Xu et
al. (2018), and in this example we apply WHAM to the same stock,
Southern New England / Mid-Atlantic Yellowtail Flounder.
Here we assume you already have wham installed. If not,
see the Introduction.
This is the 3rd wham example, which builds off model
m5 from example
2:
full state-space model (numbers-at-age are random effects for all ages,
NAA_re = list(sigma='rec+1',cor='iid'))logistic normal age compositions (
age_comp = "logistic-normal-pool0")Beverton-Holt recruitment (
recruit_model = 3)Cold Pool Index (CPI) fit as an AR1 process (
ecov$process_model = "ar1")CPI has a “limiting” (carrying capacity, Iles and Beverton (1998)) effect on recruitment (
ecov$where = "recruit",ecov$how = 2)
In example 3, we demonstrate how to project/forecast WHAM models
using the project_wham() function options for handling
fishing mortality / catch (use last F, use average F, use \(F_{SPR}\), use \(F_{MSY}\), specify F, specify catch) and the
environmental covariate (continue ecov process, use last ecov, use average ecov, specify ecov).
1. Load data
Open R and load the wham package:
For a clean, runnable .R script, look at
ex3_projections.R in the example_scripts
folder of the wham package install:
wham.dir <- find.package("wham")
file.path(wham.dir, "example_scripts")You can run this entire example script with:
write.dir <- "choose/where/to/save/output" # otherwise will be saved in working directory
source(file.path(wham.dir, "example_scripts", "ex3_projections.R"))Let’s create a directory for this analysis:
# choose a location to save output, otherwise will be saved in working directory
write.dir <- "choose/where/to/save/output"
dir.create(write.dir)
setwd(write.dir)We need the same data files as in example
2. Let’s copy ex2_SNEMAYT.dat and CPI.csv
to our analysis directory:
wham.dir <- find.package("wham")
file.copy(from=file.path(wham.dir,"extdata","ex2_SNEMAYT.dat"), to=write.dir, overwrite=TRUE)
file.copy(from=file.path(wham.dir,"extdata","CPI.csv"), to=write.dir, overwrite=TRUE)Confirm you are in the correct directory and it has the required data files:
list.files()
#> [1] "age_comp_likelihood_test_values.rds" "BASE_3"
#> [3] "CPI.csv" "ex1_SNEMAYT.dat"
#> [5] "ex1_test_results.rds" "ex11_tests.rds"
#> [7] "ex2_SNEMAYT.dat" "ex2_test_results.rds"
#> [9] "ex4_test_results.rds" "ex5_summerflounder.dat"
#> [11] "ex5_test_results.rds" "ex6_test_results.rds"
#> [13] "ex7_SNEMAYT.dat" "GSI.csv"Read the ASAP3 .dat file into R and convert to input list for wham:
asap3 <- read_asap3_dat("ex2_SNEMAYT.dat")Load the environmental covariate (Cold Pool Index, CPI) data into R:
env.dat <- read.csv("CPI.csv", header=T)2. Specify model
Setup model m5 from example
2:
full state-space model (numbers-at-age are random effects for all ages,
NAA_re = list(sigma='rec+1',cor='iid'))logistic normal age compositions (
age_comp = "logistic-normal-pool0")Beverton-Holt recruitment (
recruit_model = 3)Cold Pool Index (CPI) fit as an AR1 process (
ecov$process_model = "ar1")CPI has a “controlling” (density-independent mortality, Iles and Beverton (1998)) effect on recruitment (
ecov$where = "recruit",ecov$how = 1)
env <- list(
label = "CPI",
mean = as.matrix(env.dat$CPI), # CPI observations
logsigma = as.matrix(log(env.dat$CPI_sigma)), # CPI standard error is given/fixed as data
year = env.dat$Year,
use_obs = matrix(1, ncol=1, nrow=dim(env.dat)[1]), # use all obs (=1)
lag = 1, # CPI in year t affects recruitment in year t+1
process_model = "ar1", # fit CPI as AR1 process
where = "recruit", # CPI affects recruitment
how = 2) # limiting (carrying capacity)
input <- prepare_wham_input(asap3, recruit_model = 3,
model_name = "Ex 3: Projections",
ecov = env,
NAA_re = list(sigma="rec+1", cor="iid"),
age_comp = "logistic-normal-pool0") # logistic normal pool 0 obs
# selectivity = logistic, not age-specific
# 2 pars per block instead of n.ages
# sel pars of indices 4/5 fixed at 1.5, 0.1 (neg phase in .dat file)
input$par$logit_selpars[1:4,7:8] <- 0 # original code started selpars at 0 (last 2 rows are fixed)3. Fit the model without projections
You have two options for projecting a WHAM model:
- Fit model without projections and then add projections afterward
# don't run
mod <- fit_wham(input) # default do.proj=FALSE
mod_proj <- project_wham(mod)- Add projections with initial model fit
(
do.proj = TRUE)
# don't run
mod_proj <- fit_wham(input, do.proj = TRUE)The two code blocks above are equivalent; when
do.proj = TRUE, fit_wham() fits the model
without projections and then calls project_wham() to add
them. In this example we choose option #1 because we are going to add
several different projections to the same model, mod. We
will save each projected model in a list, mod_proj.
4. Add projections to fit model
Projection options are specifed using the proj.opts
input to project_wham(). The default settings are to
project 3 years (n.yrs = 3), use average maturity-,
weight-, and natural mortality-at-age from last 5 model years to
calculate reference points (avg.yrs), use fishing mortality
in the last model year (use.last.F = TRUE), and continue
the ecov process model (cont.ecov = TRUE). These options
are also described in the project_wham() help page.
# save projected models in a list
mod_proj <- list()
# default settings spelled out
mod_proj[[1]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=3, use.last.F=TRUE, use.avg.F=FALSE, use.FXSPR=FALSE, use.FMSY=FALSE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=TRUE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL, proj.ecov=NULL, cont.Mre=NULL, avg.rec.yrs=NULL, percentFXSPR=100, percentFMSY=100), save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[1]] <- project_wham(mod)WHAM implements four options for handling the environmental
covariate(s) in the projections. Exactly one of these must be specified
in proj.opts if ecov is in the model:
(Default) Continue the ecov process model (e.g. random walk, AR1). Set
cont.ecov = TRUE. WHAM will estimate the ecov process in the projection years (i.e. continue the random walk / AR1 process).Use last year ecov. Set
use.last.ecov = TRUE. WHAM will use ecov value from the terminal year of the population model for projections.Use average ecov. Provide
avg.yrs.ecov, a vector specifying which years to average over the environmental covariate(s) for projections.Specify ecov. Provide
proj.ecov, a matrix of user-specified environmental covariate(s) to use for projections. Dimensions must be the number of projection years (proj.opts$n.yrs) x the number of ecovs (ncols(ecov$mean)).
Note that for all options, if the original model fit the ecov
in years beyond the population model, WHAM will use these already-fit
ecov values for the projections. If the ecov model extended at
least proj.opts$n.yrs years beyond the population model,
then none of the above need be specified.
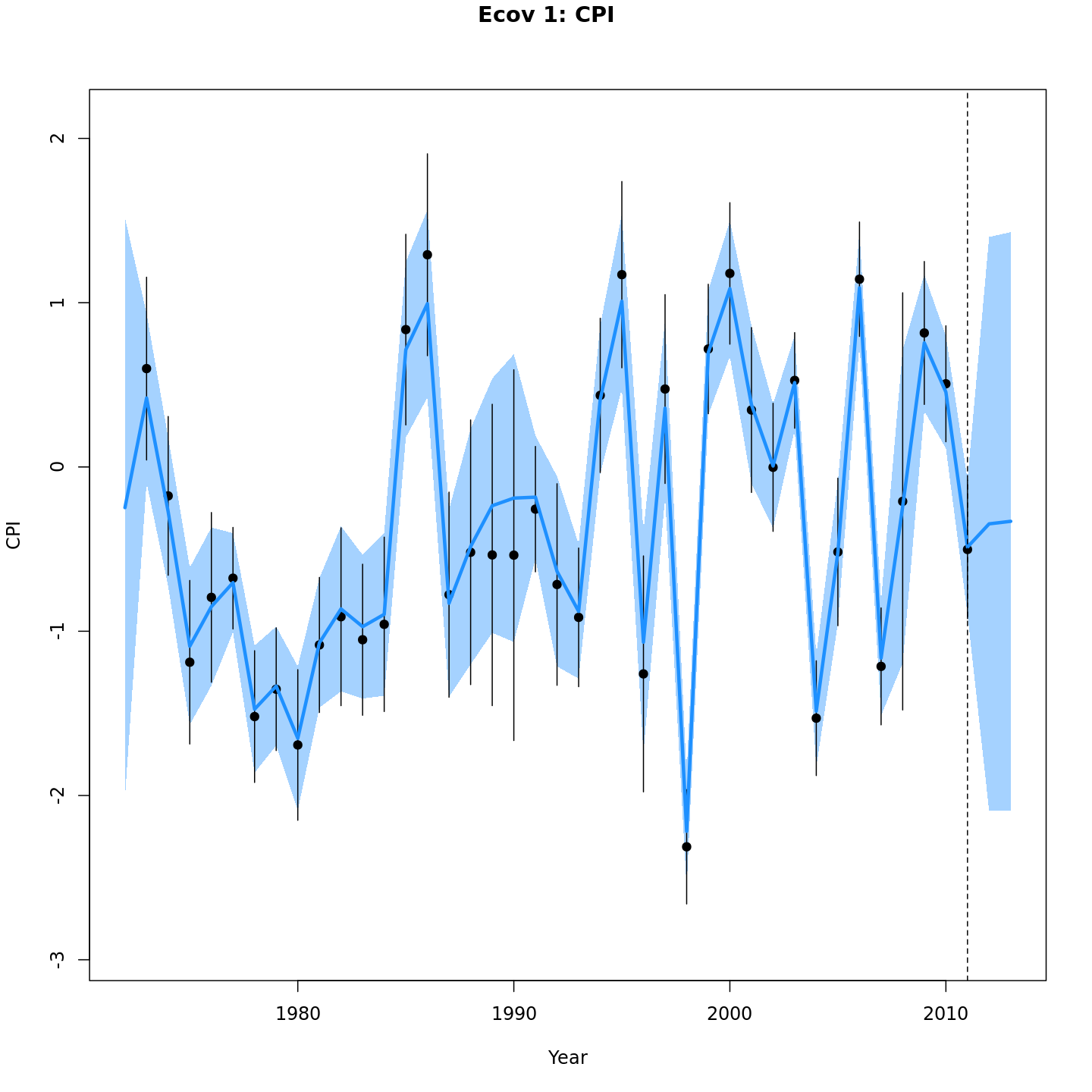
# 5 years, use average ecov from 1992-1996
mod_proj[[2]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.F=TRUE, use.avg.F=FALSE,
use.FXSPR=FALSE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=FALSE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=1992:1996, proj.ecov=NULL), save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[2]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, avg.ecov.yrs=1992:1996))
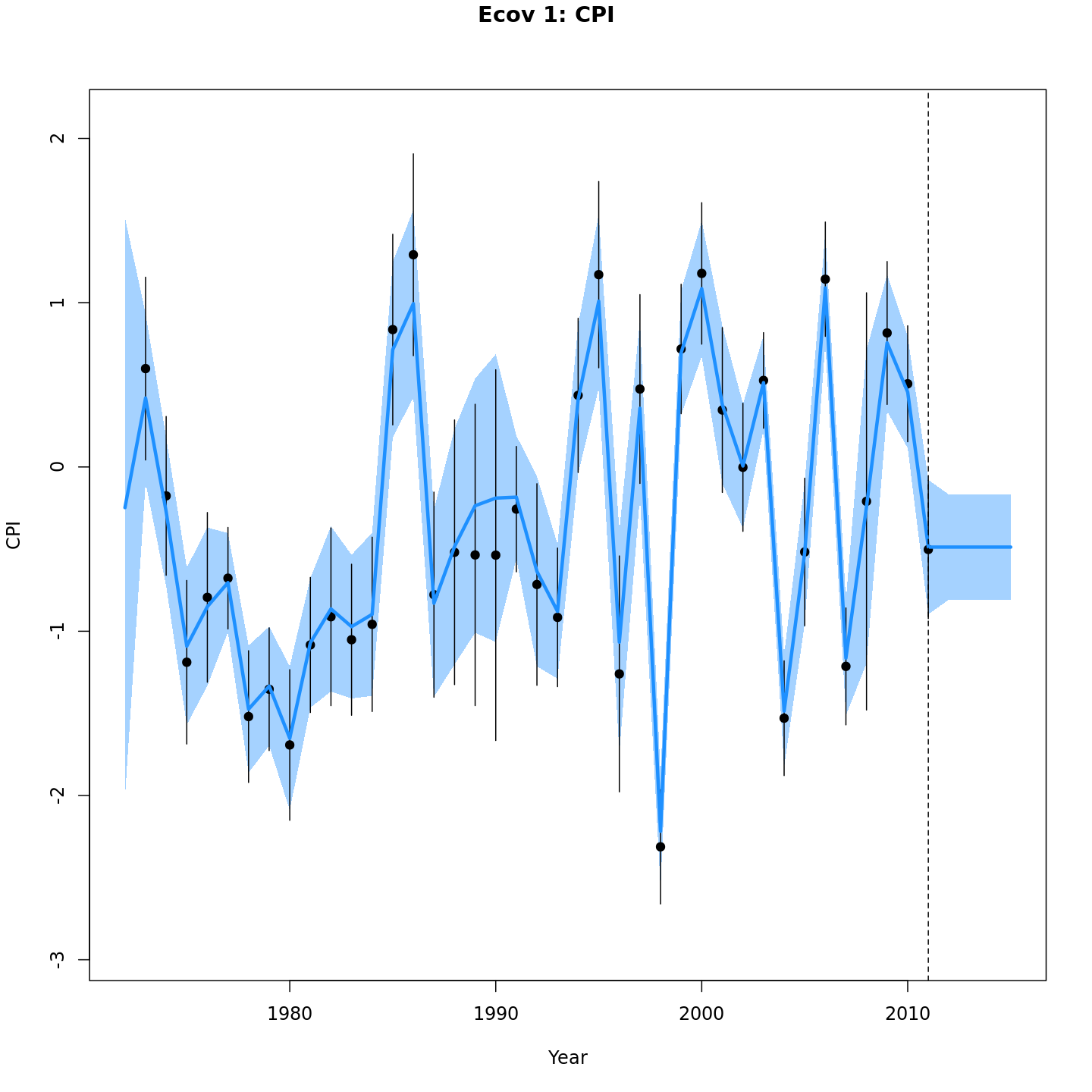
# 5 years, use ecov from last year (2011)
mod_proj[[3]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.F=TRUE, use.avg.F=FALSE,
use.FXSPR=FALSE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=FALSE, use.last.ecov=TRUE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL, proj.ecov=NULL), save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[3]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.ecov=TRUE))
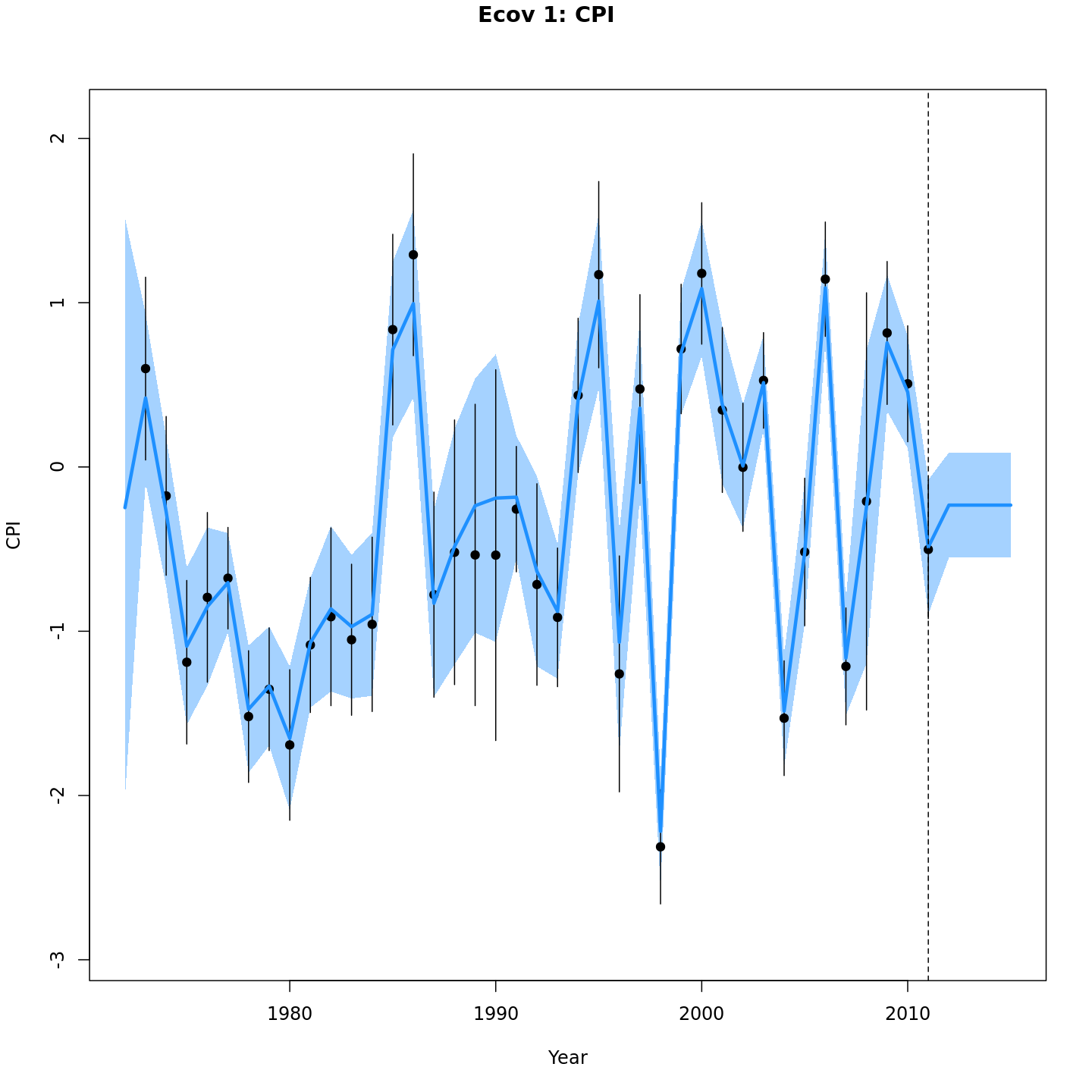
# 5 years, specify high CPI ~ 0.5
# note: only need 4 years of CPI because CPI in last model year (2011) was already fit,
# and CPI affects recruitment with lag = 1. I.e., to project model 5 years (2012-2016),
# need CPI from 2011-2015 and CPI_2011 already exists in initial model fit.
mod_proj[[4]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.F=TRUE, use.avg.F=FALSE,
use.FXSPR=FALSE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=FALSE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL,
proj.ecov=matrix(c(0.5,0.7,0.4,0.5),ncol=1)),
save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[4]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, proj.ecov=matrix(c(0.5,0.7,0.4,0.5),ncol=1)))
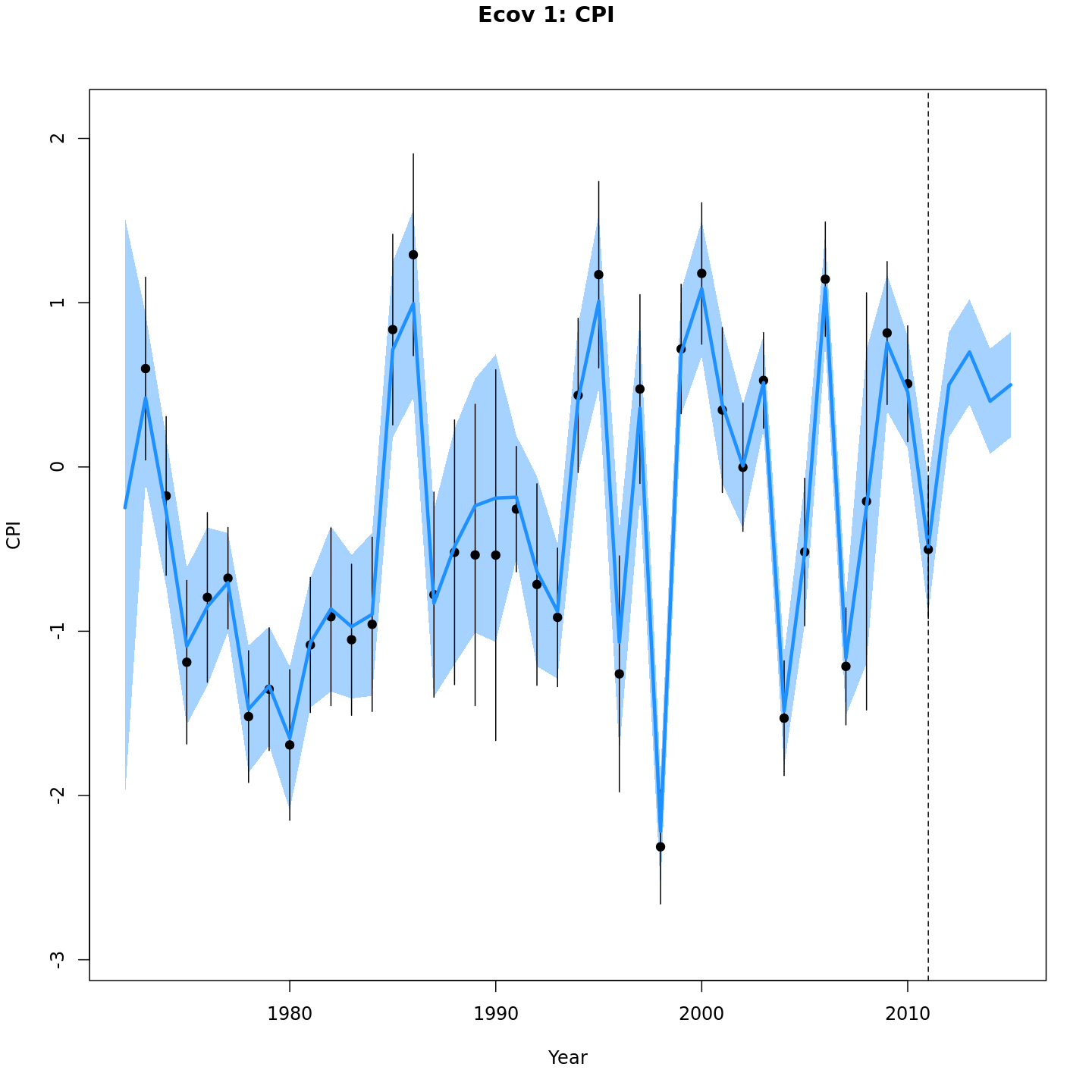
# 5 years, specify low CPI ~ -1.5
# note: again, only need 4 years of CPI because CPI in last model year (2011) was already fit,
# and CPI affects recruitment with lag = 1. I.e., to project model 5 years (2012-2016),
# need CPI from 2011-2015 and CPI_2011 already exists in initial model fit.
mod_proj[[5]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.F=TRUE, use.avg.F=FALSE,
use.FXSPR=FALSE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=FALSE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL,
proj.ecov=matrix(c(-1.6,-1.3,-1,-1.2),ncol=1)),
save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[5]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, proj.ecov=matrix(c(-1.6,-1.3,-1,-1.2),ncol=1)))WHAM implements six options for handling fishing mortality in the
projections. Exactly one of these must be specified in
proj.opts:
(Default) Use last year F. Set
use.last.F = TRUE. WHAM will use F in the terminal model year for projections.Use average F. Set
use.avg.F = TRUE. WHAM will use F averaged overproj.opts$avg.yrsfor projections (as is done for M-, maturity-, and weight-at-age).Use F at X% SPR. Set
use.FXSPR = TRUE. WHAM will calculate and apply F at X% SPR, where X was set byinput$data$percentSPR(default = 40%). There is also a percentFXSPRSpecify F. Provide
proj.F, an F vector with length =proj.opts$n.yrs.Specify catch. Provide
proj.catch, a vector of aggregate catch with length =proj.opts$n.yrs. WHAM will calculate F across fleets to apply the specified catch.Use F that provides MSY. Set
use.FMSY = TRUE. WHAM will calculate and apply F at MSY. There is a check to make sure that a stock-recruit model is assumed and, if not, F at X% SPR is used instead.
# 5 years, specify catch
mod_proj[[6]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.F=FALSE, use.avg.F=FALSE,
use.FXSPR=FALSE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=c(10, 2000, 1000, 3000, 20), avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=TRUE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL, proj.ecov=NULL), save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[6]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, proj.catch=c(10, 2000, 1000, 3000, 20)))
# 5 years, specify F
mod_proj[[7]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.F=FALSE, use.avg.F=FALSE,
use.FXSPR=FALSE, proj.F=c(0.001, 1, 0.5, .1, .2), proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=TRUE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL, proj.ecov=NULL), save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[7]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, proj.F=c(0.001, 1, 0.5, .1, .2)))
# 5 years, use FXSPR
mod_proj[[8]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.F=FALSE, use.avg.F=FALSE,
use.FXSPR=TRUE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=TRUE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL, proj.ecov=NULL), save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[8]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.FXSPR=TRUE))
# 3 years, use avg F (avg.yrs defaults to last 5 years, 2007-2011)
mod_proj[[9]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=3, use.last.F=FALSE, use.avg.F=TRUE,
use.FXSPR=FALSE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=TRUE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL, proj.ecov=NULL), save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[9]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(use.avg.F=TRUE))
# 10 years, use avg F 1992-1996
mod_proj[[10]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=10, use.last.F=FALSE, use.avg.F=TRUE,
use.FXSPR=FALSE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=1992:1996,
cont.ecov=TRUE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL, proj.ecov=NULL), save.sdrep=FALSE)
# equivalent
# mod_proj[[10]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=10, use.avg.F=TRUE, avg.yrs=1992:1996))
# 5 years, use $F_{MSY}$
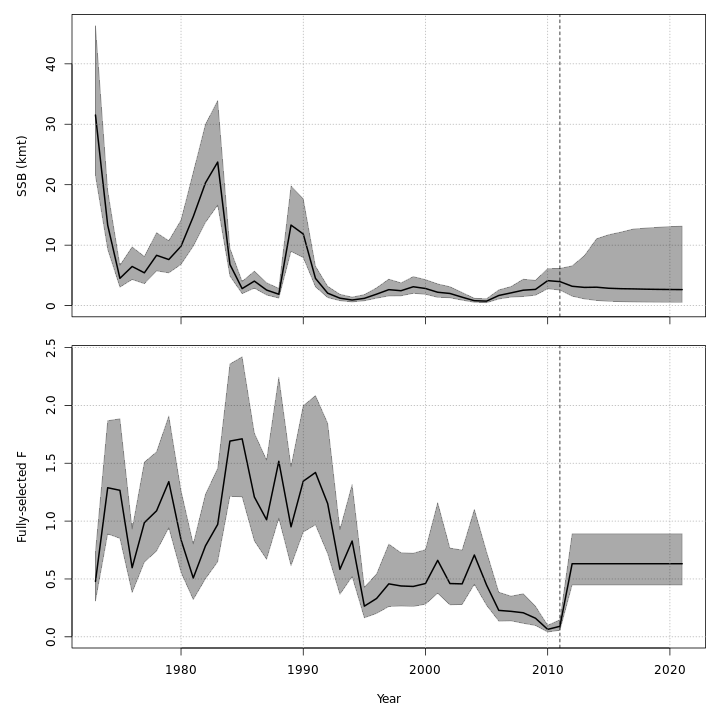
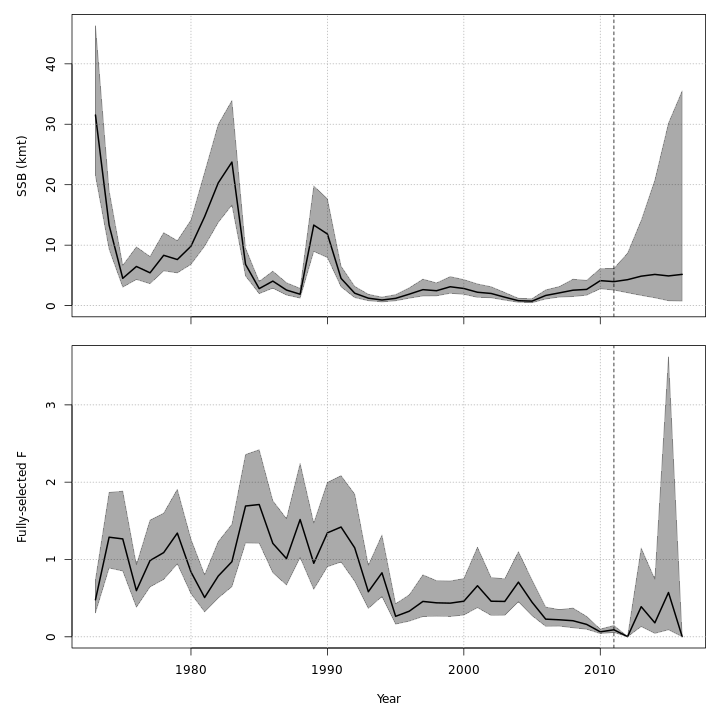
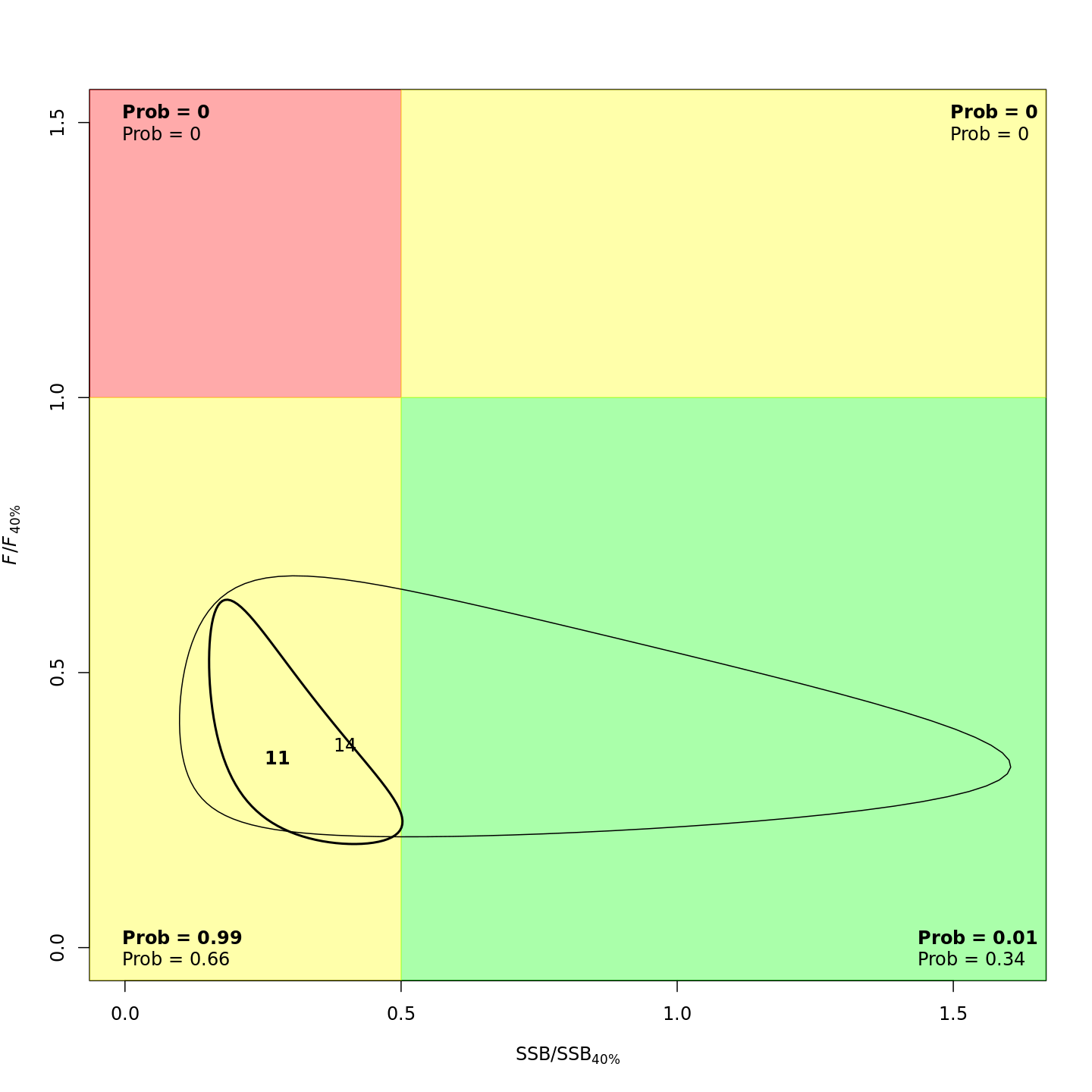
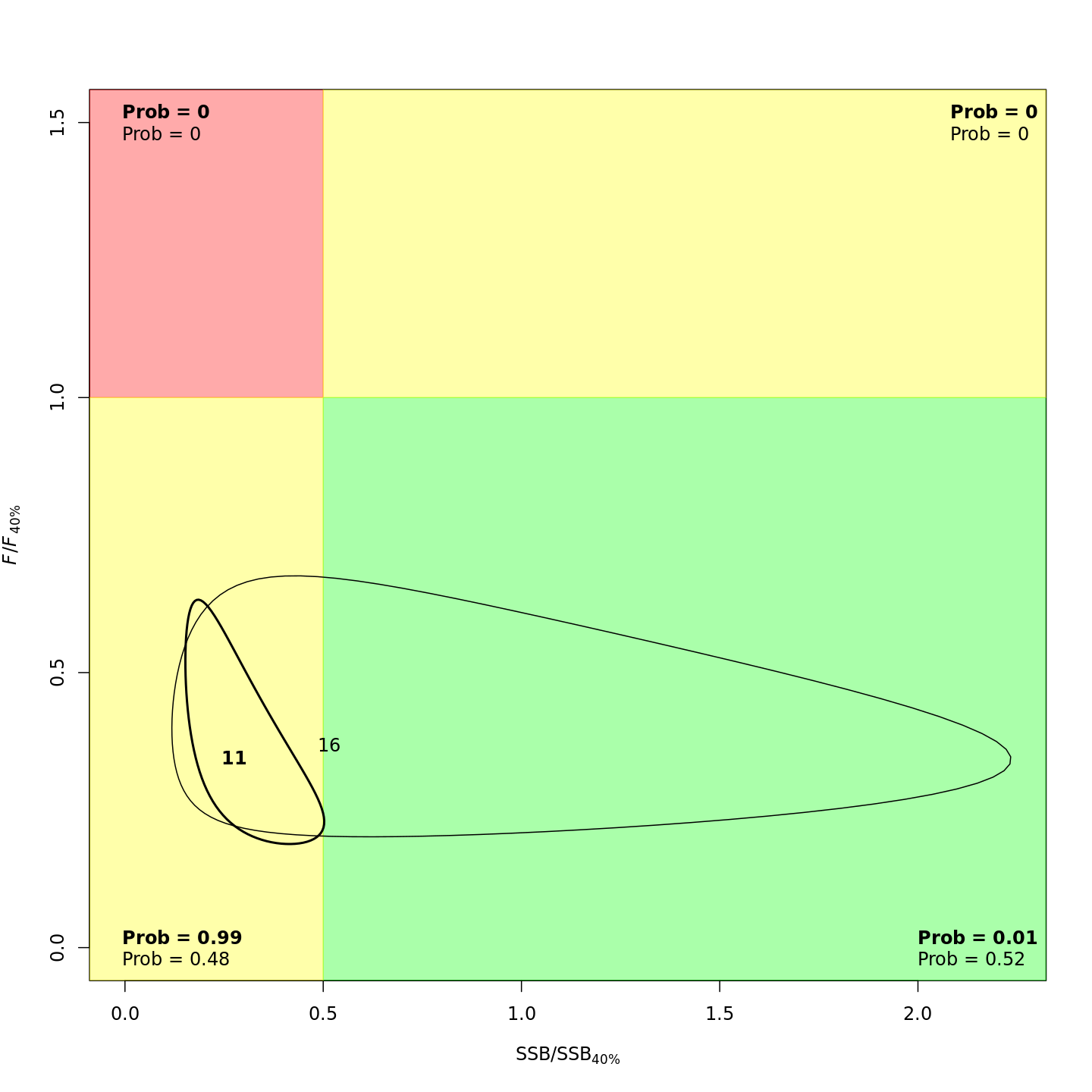
mod_proj[[11]] <- project_wham(mod, proj.opts=list(n.yrs=5, use.last.F=FALSE, use.avg.F=FALSE,
use.FMSY=TRUE, proj.F=NULL, proj.catch=NULL, avg.yrs=NULL,
cont.ecov=TRUE, use.last.ecov=FALSE, avg.ecov.yrs=NULL, proj.ecov=NULL), save.sdrep=FALSE)Save projected models
saveRDS(mod_proj, file="m5_proj.rds")5. Compare projections
The models with projections are evaluated to obtain optimized random effects but they do not need to be refitted with projections added because the observations and marginal likelihood do not change. However, we can confirm that the NLL is the same for all projected models (within some tolerance).
mod$opt$obj # original model NLL#> [1] -829.4137
#> attr(,"logarithm")
#> [1] TRUE
nll_proj <- sapply(mod_proj, function(x) x$opt$obj) # projected models NLL
round(nll_proj - mod$opt$obj, 6) # difference between original and projected models' NLL#> [1] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0Now let’s plot results from each of the projected models.
for(m in 1:length(mod_proj)){
plot_wham_output(mod_proj[[m]], dir.main=file.path(write.dir,paste0("proj_",m)), out.type='html')
}To more easily compare the same plots for each projection, we can copy the plots into new folders organized by plot type instead of model.
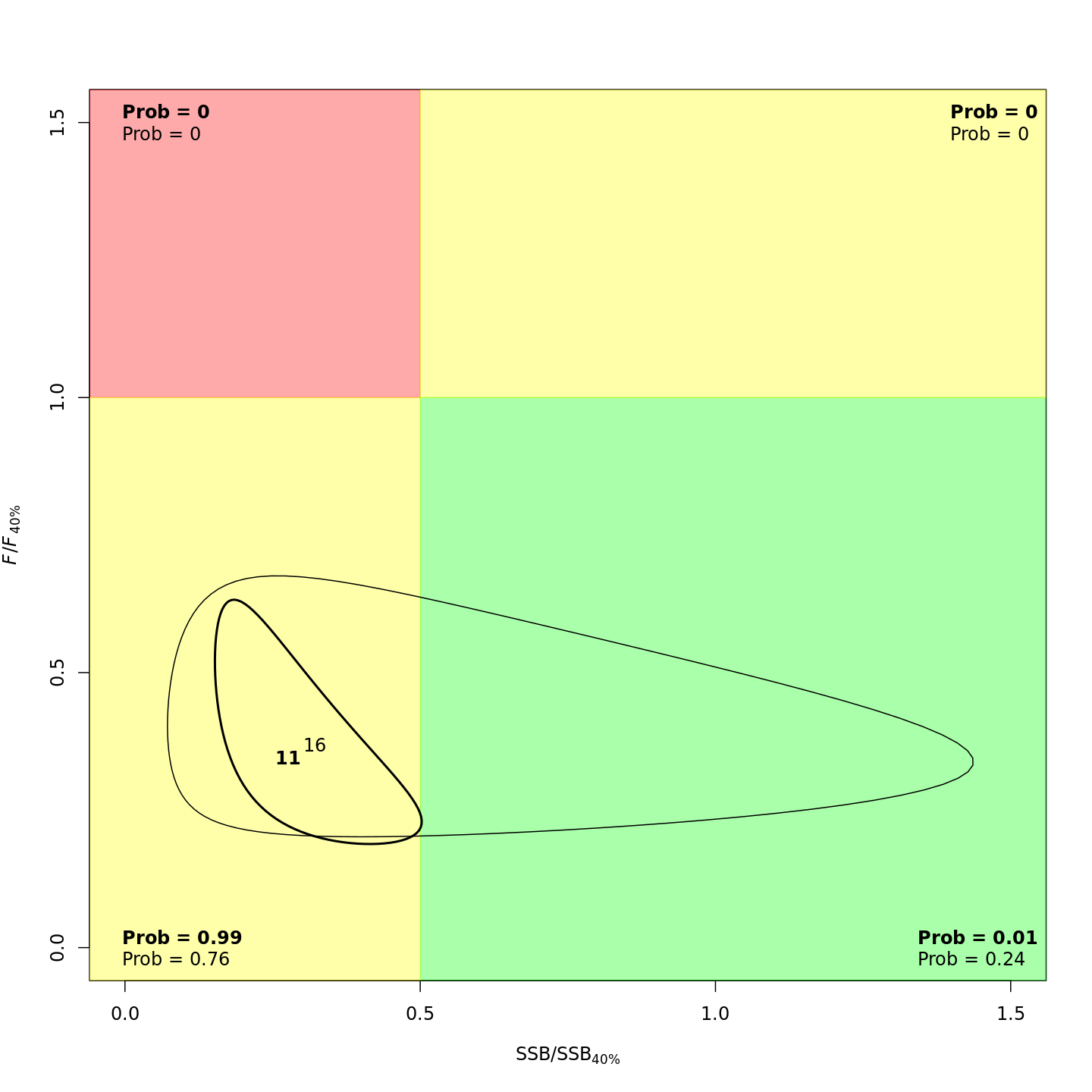
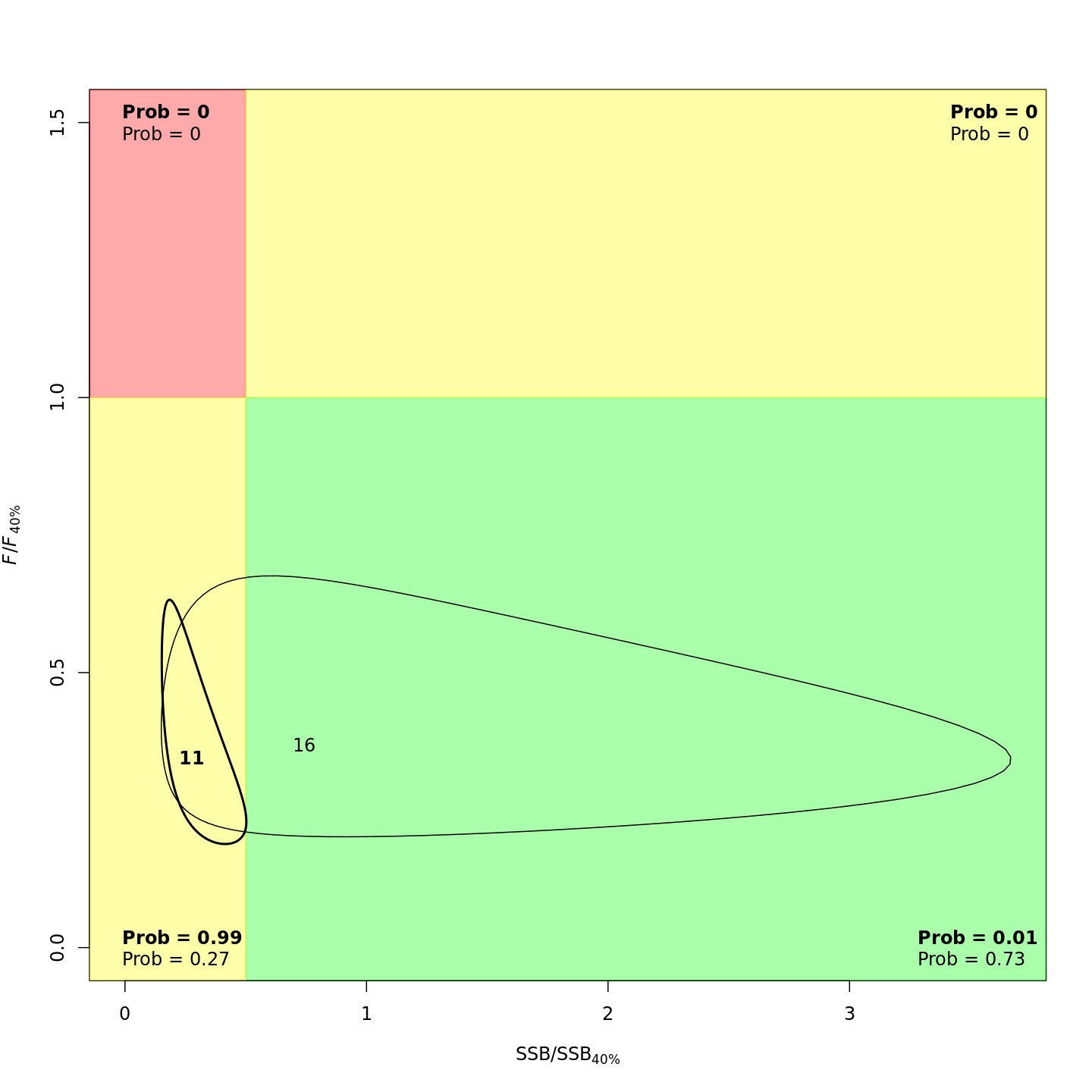
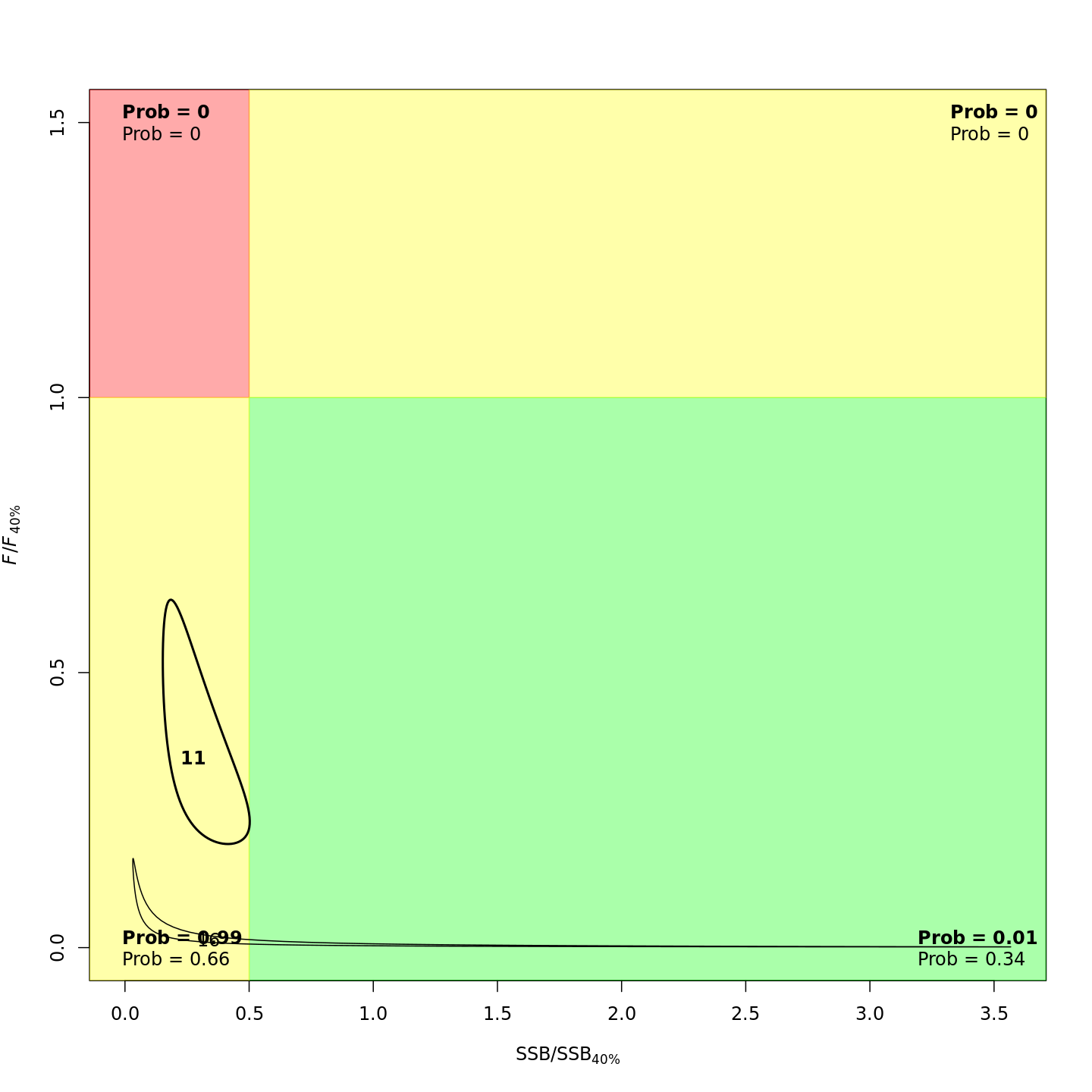
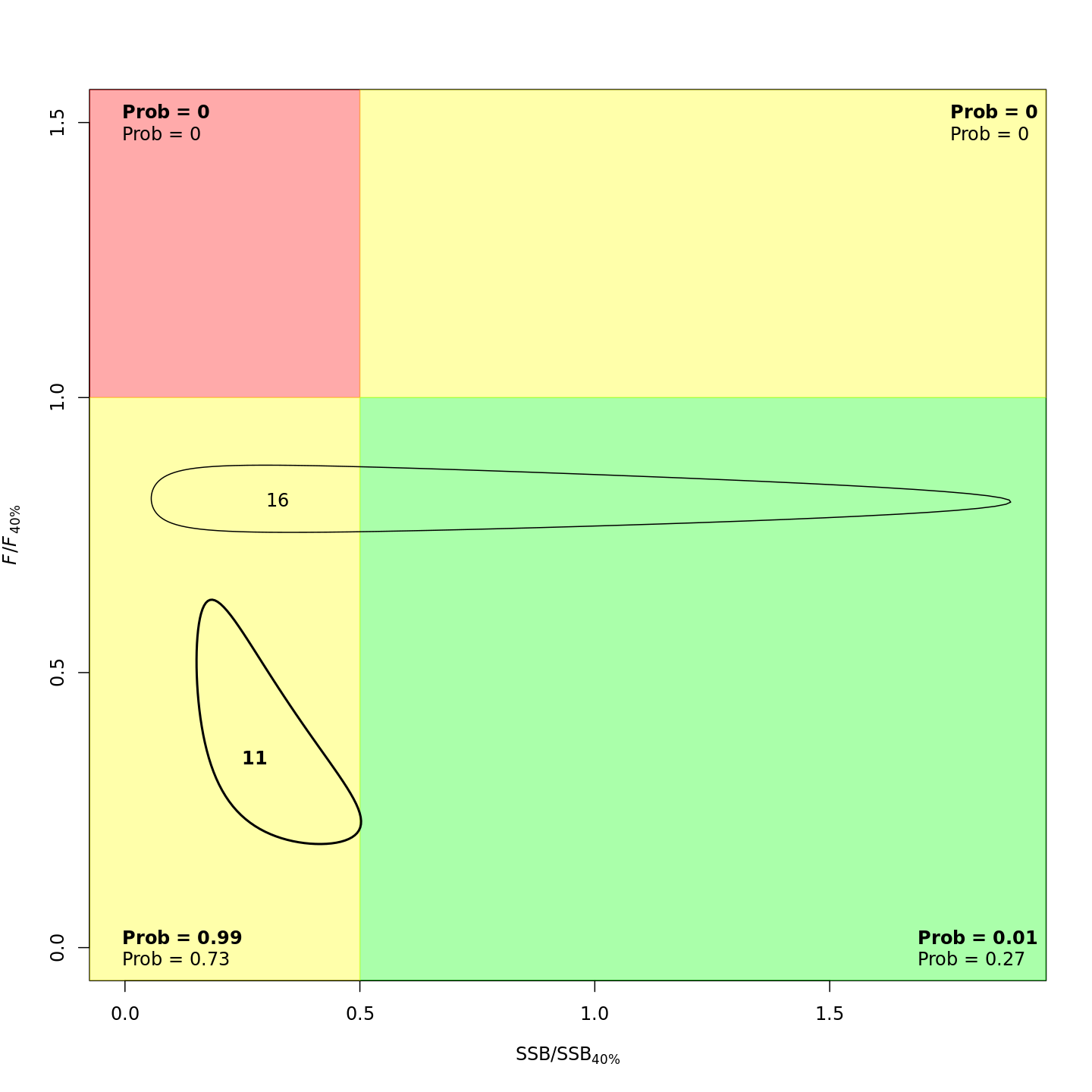
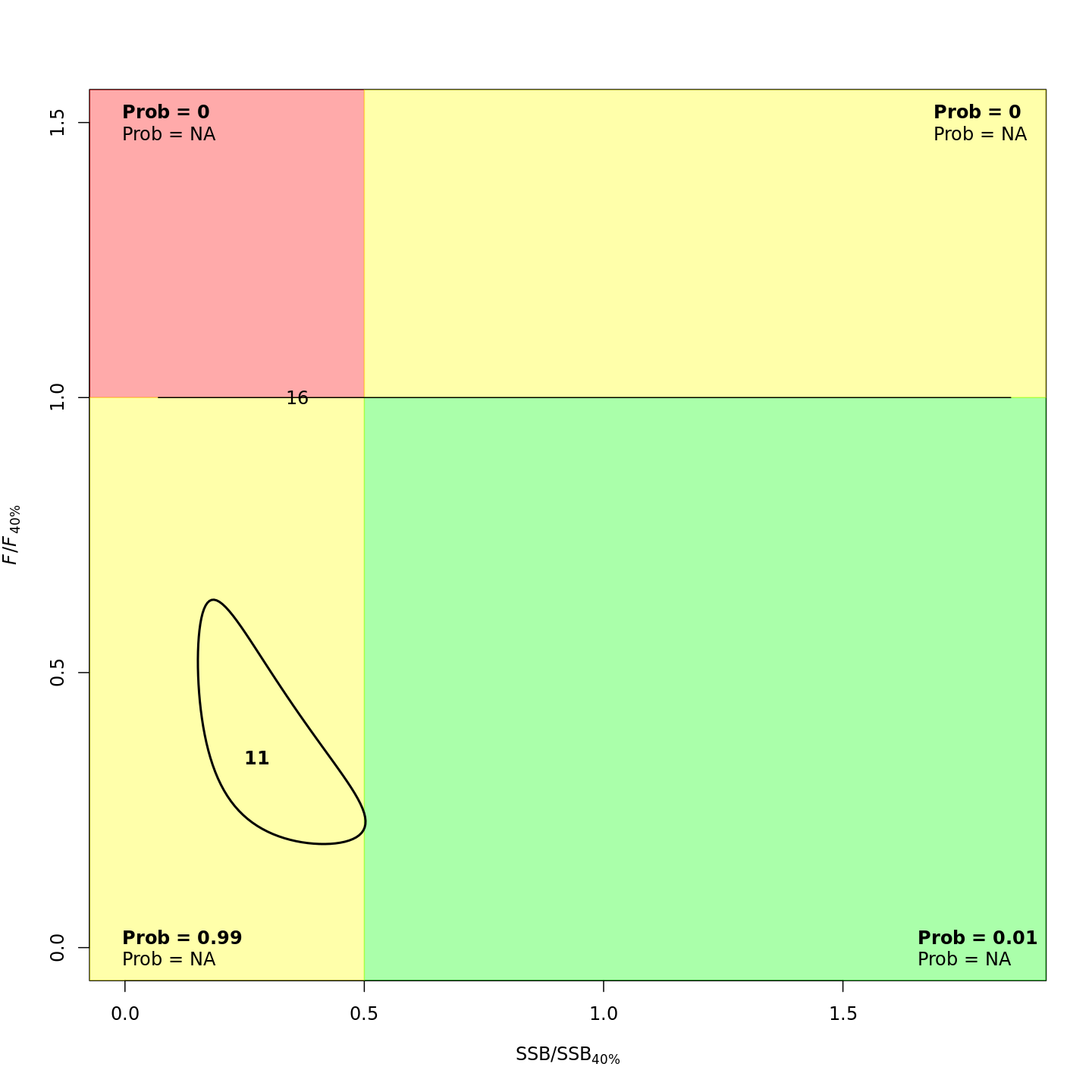
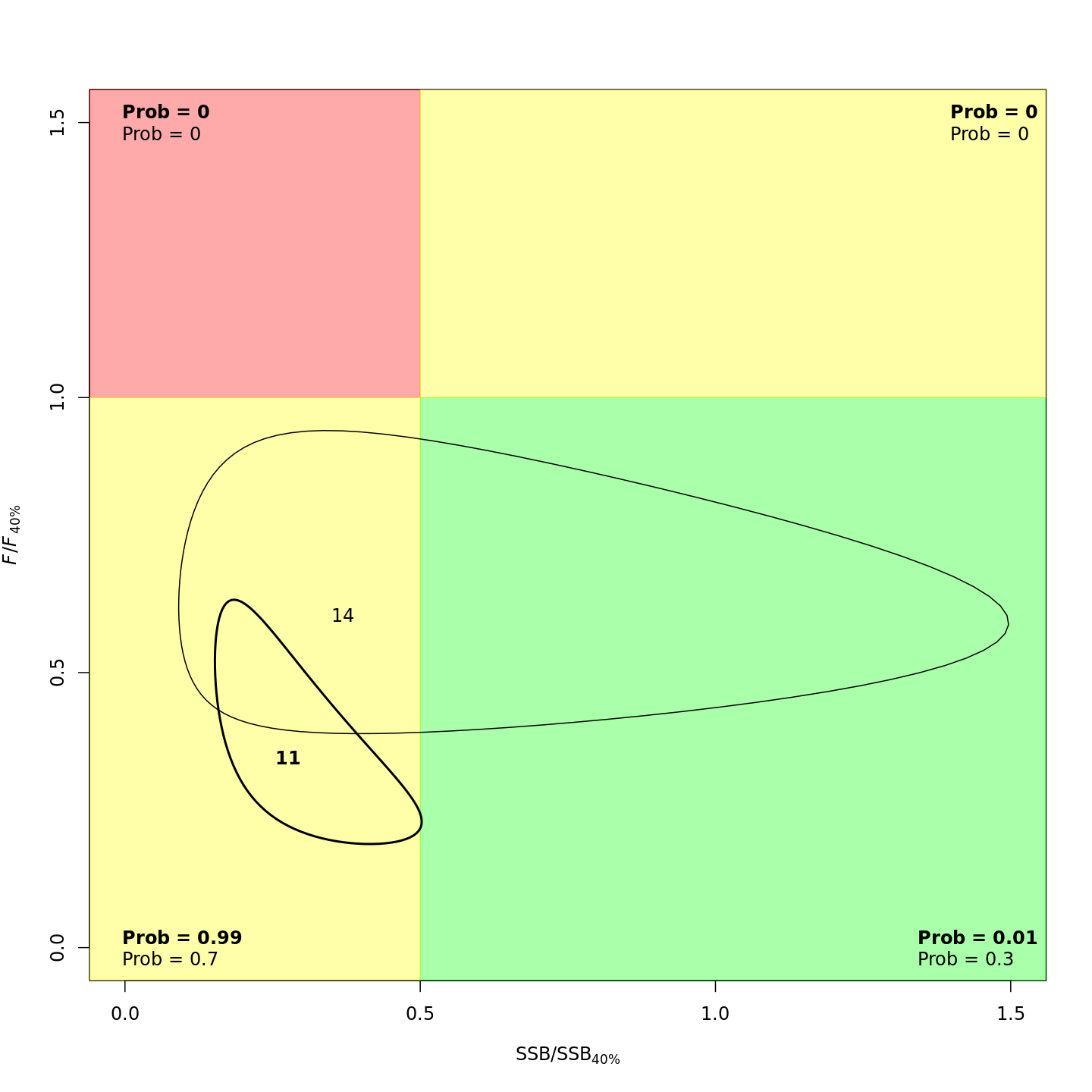
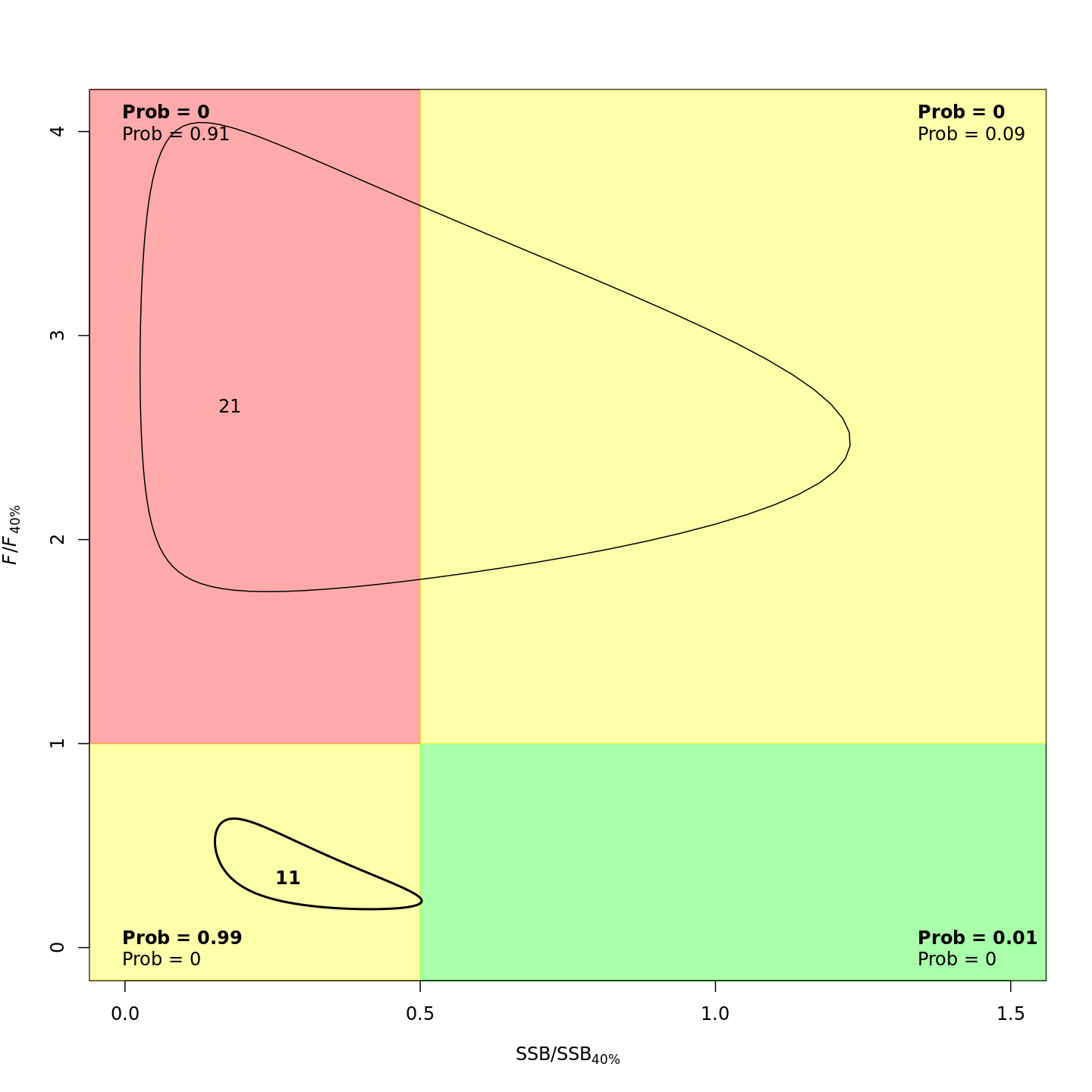
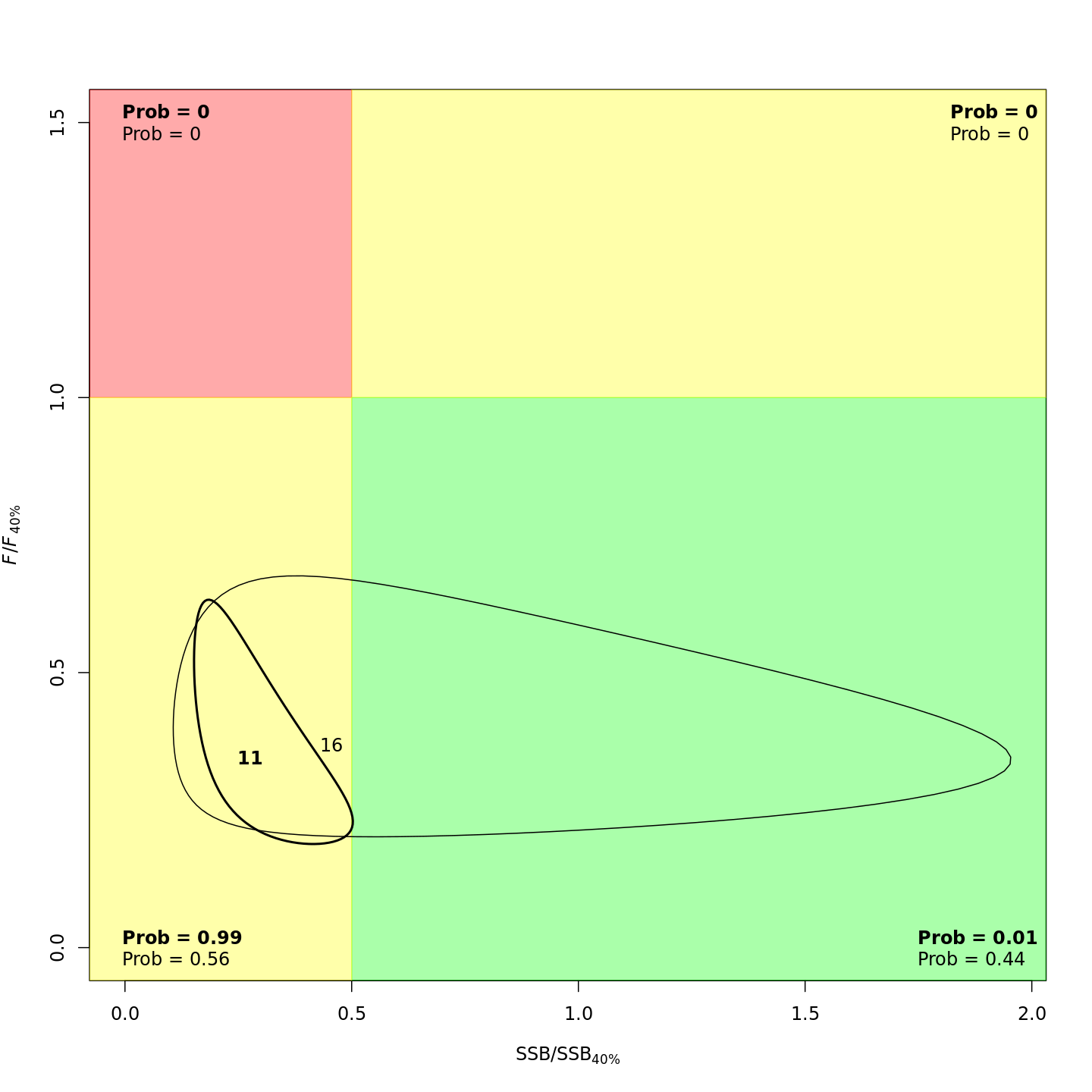
plots <- c("Ecov_1","F_byfleet","SSB_at_age","SSB_F_trend","SSB_Rec_time","Kobe_status")
dirs <- file.path(write.dir,plots)
lapply(as.list(dirs), FUN=dir.create)
for(m in 1:length(mod_proj)){
for(i in 1:(length(plots)-1)){
file.copy(from=file.path(write.dir,paste0("proj_",m),"plots_png","results",paste0(plots[i],".png")),
to=file.path(dirs[i],paste0(plots[i],"_proj_",m,".png")))
}
file.copy(from=file.path(write.dir,paste0("proj_",m),"plots_png","ref_points","Kobe_status.png"),
to=file.path(dirs[i+1],paste0(plots[i+1],"_proj_",m,".png")))
}